Last updated on May 19, 2024
When you first start playing backgammon you will encounter a bewildering amount of terminology that may be difficult to comprehend. Backgammon is like any other organised area of life, there is a unique set of jargon and terminology that is associated. It takes time to learn the backgammon language. In this Deluxe Backgammon post for beginners, we will take a look at some common backgammon terms.
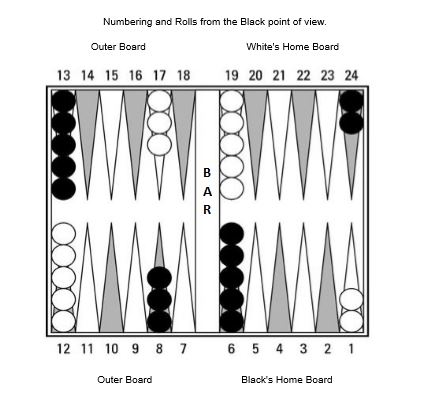
Home board/outer board
The home board is the last quadrant where checkers need to move to before they can be borne off. There are two home boards and opposite them are the outer boards.
Bar
The bar is located at the very centre of the backgammon board and is labelled on the image above. Typically, it is that ridge that divides the backgammon board in two. Incidentally, this is where the board folds in half, that is if the backgammon board is the attaché type. Every checker that is hit is sent to the bar which is a holding zone for all checkers before re-entering into a home board.
Points
Backgammon is a game played by two players, each with fifteen checkers, on a board consisting of 24 narrow triangles called points. The players move their checkers around the points according to the roll of the dice and the first player to get all their checkers off is the winner.
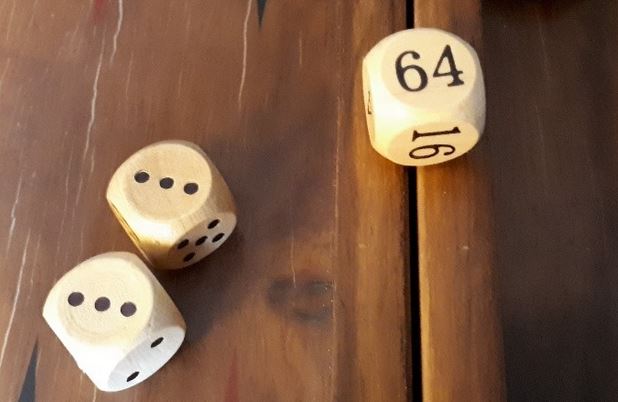
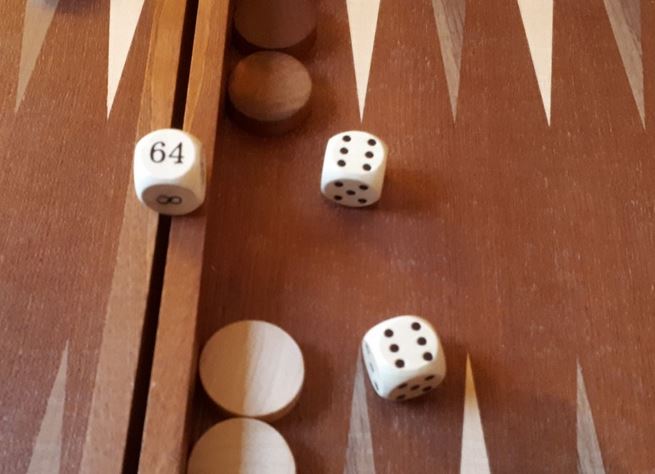
Doubling cube
Most backgammon sets include a doubling cube, which is a die, typically larger than regular dice. It has the numbers 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 marked on its faces. It is used for keeping track of the increase in stakes of the game and the player who next has the right to double. At the start of the game, the doubling cube will be placed on the bar with the number 64 displayed. At this point, the value of the cube is effectively 1.
Despite, the number 64, it starts representing a value of 1. Once a player feels that they have an advantage in the game they can offer the doubling cube to their opponent. If the opponent accepts this offer then the points for the game are doubled and the opponent keeps the cube on their side of the board, reserving the right to redouble. If the opponent rejects the offer to double, they immediately lose at the current game value. There is no limit to how many times the stakes can be doubled.
Secure a point/make a point
Securing or making a point simply means taking control of certain points on the backgammon board. This is done by landing at least two checkers on any of the points on the board. Opposing checkers cannot land on secured points. A secured point in the opponent’s home board is known as an anchor and provides a safe landing point for checkers -re-entering from the bar. As well as providing a safe landing zone, secured points provide obstacles that can block an opponent’s checkers.
Blots
Blots are single or solitary checkers on a point. These are vulnerable to attack and opposing checkers can land on them, or in backgammon terminology, hit them, and send them to the bar. The opposing checker then needs to re-enter from the bar before any other checkers can be moved.
Hit
To hit is to land one of your checkers on an opposing blot. The checker that was hit will be moved over to the bar making it start all over again. Hitting is an important tactical move in backgammon since it delays the opponent’s progress in the race.
Prime
A prime is a connected row of secured points. These secured points are built side by side for the purpose of containing or trapping opposing checkers. A 6-prime is the ideal blocking mechanism as any opposing checker behind the wall is trapped until the 6-prime is deconstructed.
Builder
A builder is a checker brought down from the outer board which will be used to secure or make a point in a subsequent turn.
Anchor
A point occupied in the opponent’s home board by two or more checkers. The anchor provides a safe landing place for checkers entering after being hit. An anchor occupying the 3 to 5-points are called advanced anchors. If the anchor occupies the 1 or 2-point it is called a deep anchor.
Timing
Timing refers to whether a player’s position is likely to improve or deteriorate over time. It most commonly refers to being behind in the race when a player would like to maintain their board structure without crunching while waiting for a shot.
Gammons and backgammons
If a player bears off all fifteen of their checkers before their opponent has borne off any of theirs, they win by a gammon or two-point game. If a player bears off all fifteen of their checkers before their opponent has borne off any of theirs and they have one or more checkers in the player’s home board or on the bar, they win by a backgammon or 3-point game.
Hopefully, you have learnt what some of the common backgammon terms mean.
Related content
Setup and rules FAQs are available on this link.
Common backgammon terms from Gammon Life.




How common are gammons and backgammons?
A backgammon is fairly rare, perhaps only happening in 1% of backgammon games. A gammon is more frequent, occurring in perhaps 10% of backgammon games.