Last updated on April 20, 2024
This is an introductory backgammon glossary and is by no means complete. It will be added to over time. Also, refer to our FAQ post for additional information. A complete list of Playing Guides is available on this link.
Anchor
A point occupied by two or more of your checkers in or around the opponent’s home board. This is a secure landing space for other checkers and also represents a barrier to movement and re-entry.
Advanced Anchor
An anchor on the opponent’s five-point, four-point, or sometimes the bar-point. Advanced anchors are good because they give a player more opportunities to hit the opponent’s checkers and they give the player a better opportunity to escape their own checkers.
Action Play
A play designed to provoke an exchange of hits, typically used after the opponent has escaped his runners.
Ahead in the Count/Race
Having a lower pip count than your opponent; see pip count.
Backgammon
A game in which one player bears off all of his checkers while his opponent still has one or more checkers on the bar or in the winner’s home board. A win by a backgammon triples the stakes of the game.
Back game
A strategy of occupying two or more points in one’s opponents home board. This strategy is usually employed by a player who is substantially behind in the race. The back-game player tries to hold both anchors as long as possible and force his opponent to bear in or bear off awkwardly. The idea is to hit a late shot and then contain the hit checker behind a prime.
Back Man
A player’s rearmost checker.
Baffle box
A device placed at the edge of the board consisting of a number of angled bars of wood enclosed in a box casing. Each player must shake their dice in their cup and then into the baffle box. The box completely eliminates the possibility of dice manipulation.
Bar
The area where checkers are placed after being hit, it is usually, a raised divider between the home boards and outer boards.
Bar point
The bar point is either of the two points in the outer board adjacent to the bar; the 7-point or the 18-point.
Bear off
To remove a checker from the board according to a roll of the dice after all of your checkers have been brought into your home board. The first player to bear off all 15 of their checkers is the winner.
Blitz
An all-out attack on enemy blots in your home board aimed at closing out your opponent. This strategy is best applied after an early hit or hits against your opponent.
Block
A point occupied by two or more checkers on the home board or the outer board.
Blot
A single checker which is vulnerable to being hit.
Builder
A builder is a checker brought into the outer board within range of one or more key points that you want to secure.
Breaking contact
In backgammon, the concept of breaking contact is to move past the last of the opponent’s checkers, so that no further hitting is possible.
Checker
One of the 15 playing pieces allocated to each player. The sets of checkers will always be of different colours.
Chouette
Chouette is a form of backgammon for more than two players. In a chouette, one person, called the Box, plays a game of backgammon for points against a team of other players headed by the Captain, who rolls the dice and plays the checkers for the team.
Closeout position
A position where an opponent has one or more checkers on the bar and a player has made all the points in their home board, so the opponent can’t re-enter. A closed board is when a player has all the points in their home board secured.
Contact
The condition under which each player has checkers remaining which have not passed those of their opponent. Blots may be hit whilst there is still contact in the game.
Cover
To make a block on a single point.
Crawford game
The first game in a match wherein one player is within a single point of winning the match. It is in this game that the Crawford rule applies.
Crawford rule
A rule which forbids the doubling cube to be used for the first game after one player has reached a score exactly one point less than the objective score for a match.
Crunch (Crunching)
Where you are forced to abandon favourable points due to the lack of alternate options. For example, a play in which you are forced to break down a secure point and move your checkers deep within your home board where they have little strategic value.
Deep Anchor
An anchor on the opponent’s one-point or two-point.
Double
To offer the doubling cube, therefore doubling the stakes of the current game.
Doubles
A dice roll in which both values are identical, e.g. 5-5.
Doubling cube
A six-sided die which is not rolled, but is marked with powers of two (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64) and used to track the stakes of the current game.
End Game
The phase of a game which begins when one of the players begins to bear off.
Equity
Equity is the value of ownership. In backgammon, it means either the value of a player’s game or their chances of winning the match.
Five point
The 5-point is strategically the most important position on the board. Holding the 5-point conveys a considerable advantage in the game. Your opponent’s 5-point is your 20-point.
Full Prime
A prime of six consecutive points that completely blocks the opponent from moving checkers as the highest possible dice roll is six.
Gammon
A game in which one player removes all their checkers before their opponent can remove any. A win by a Gammon doubles the stakes on the game.
Golden Points
The five-point is the Golden Point as designated by Paul Magriel in his 1976 book, Backgammon. It is the most important point on the board. The Golden Anchor is your opponent’s 5-point, your 20-point, which is a useful position for preventing primes when it is occupied by two of your own checkers.
Hit
To move onto a point occupied by an opposing blot, and move the hit checker to the bar.
Home board
The portion of the board containing points 1-6. The checkers need to move here before they can be borne off. It is also the part of the board where the opponent’s checkers are re-entered from the bar. Also known as the Inner board.
Inner board
See Home board.
Jacoby rule
The Jacoby rule permits gammons and backgammons to count for double and triple stakes only if at least one player has doubled during the game.
Match
A series of games of backgammon. The match is played until one competitor reaches a predetermined score.
Mid-point
Either of the two points furthest from the bar; the 12-point or the 13-point.
Money play
Money play is the standard style of competition in backgammon in which games are played individually and the players bet on the result. At the end of each game, the loser pays the winner the agreed initial stake multiplied by the value of the doubling cube and multiplied by 2 for a gammon or 3 for a backgammon.
No Dice
Cocked dice. One, or possibly both of the dice, had failed to land perfectly flat. Both dice must be re-rolled.
Normalized Match Score
A match score is expressed in terms of the number of points needed by both players to win the match. For instance, ‘2-away/4-away’ (or: -2/-4) could indicate the state of a seven-point match in which one party has won five points and the other side three points.
Notation
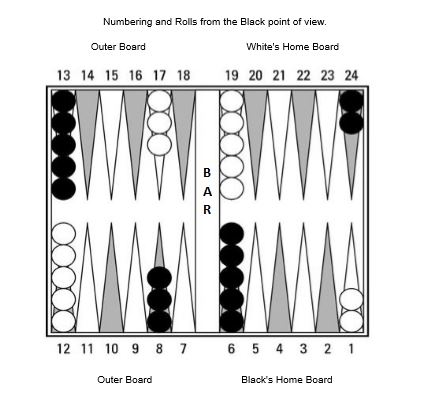
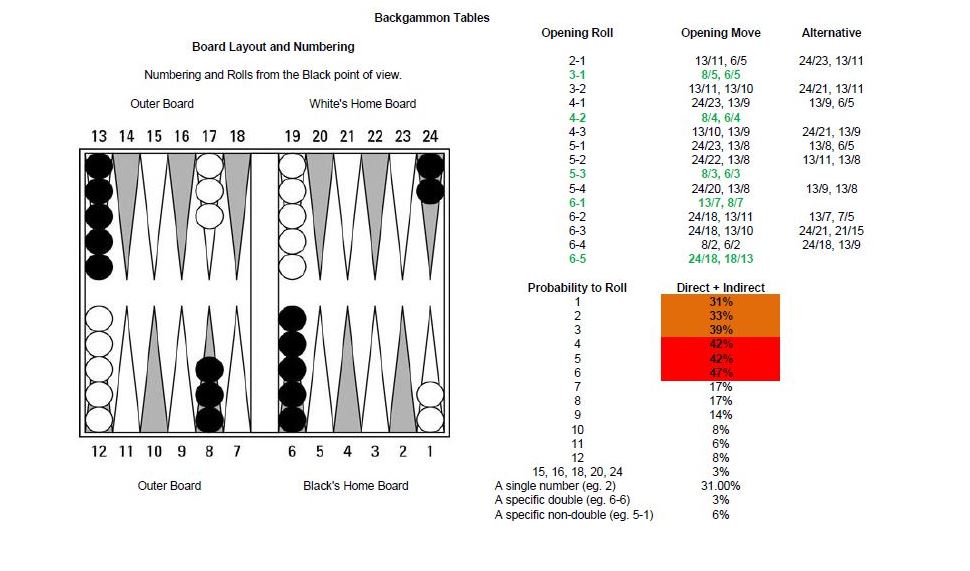
In backgammon, the common way of describing the movement of checkers involves numbering the points around the board from 24 to 1 such that the numbers diminish when the checkers move towards the home board. This implies that a reverse numbering applies when the opponent is on roll (with the 24-point now referred to as the 1-point, etc.). A move of a single checker is indicated by the start and the end number separated by a slash. If a move results in a checker being hit, this is indicated by adding an asterisk to the number on which a checker was hit.
Open point
A point a player can move their checkers to. An open point is not occupied by more than one opposing checker.
Pip
One of the markings on the face of a die. Each pip corresponds to a movement of one point.
Pip count
The total number of remaining pips needed to bear off all checkers from the board.
Point
One of the twenty-four narrow triangles on the backgammon board where the players’ checkers move.
Prime
Several consecutive secure points held by a player.
Race
A game in which there is no longer contact. The result is then dependent on the rolls of the dice.
Recirculation
Recirculation is a process whereby you deliberately leave a blot to be hit in order to improve your timing. It may seem counterproductive, but it can be a very useful tactic when behind in the race. It will hopefully open up chances of a return hit against your opponent.
Slot
Slotting is where a single checker is moved to a point that you wish to secure on a subsequent roll. Slotting is a useful tactic to help build primes.
Split
To break up two checkers which are together on a point and leave them as blots. Splitting generally refers to the back checkers.
Tactics
Short-term aspects of the game, as opposed to overall strategic considerations. Tactics in backgammon include hitting blots, making points, splitting and clearing points.
Take
Accept a double.
Tavla
Tavla is a Turkish game similar to Western backgammon. The board is identical to backgammon, with 24 points, but the rules differ slightly.
Timing
Timing refers to whether a player’s position is likely to improve or disintegrate over time. It most commonly refers to being behind in the race when a player would like to maintain their board without crunching while waiting for a shot.
Underplay
To make a safe, timid play when a stronger play is available.
Unstack
To move checkers from a heavily stacked point.
Volunteer a Shot
Purposely leave a blot within range of being hit now rather than be forced to leave it later when the danger may be greater.
Walk a Prime
Roll a prime. To move a prime forward whilst maintaining its structural integrity.





useful, I’ve been playing backgammon since I was ten and there were a few terms I’ve never heard of before.